Project formulas
Project formulas provide a way to create reusable calculations and logic that can be accessed from any page or component in your project. Unlike component-level formulas that are only available within a specific component, project formulas can be used throughout your entire application.
When to use project formulas
Project formulas are ideal for:
- Common calculations used across multiple components
- Shared data transformations
- Utility functions like date formatting or number parsing
- Business logic that needs to be consistent throughout the application
- Complex operations that might be reused
Using project formulas ensures consistency in your application and reduces duplication of code.
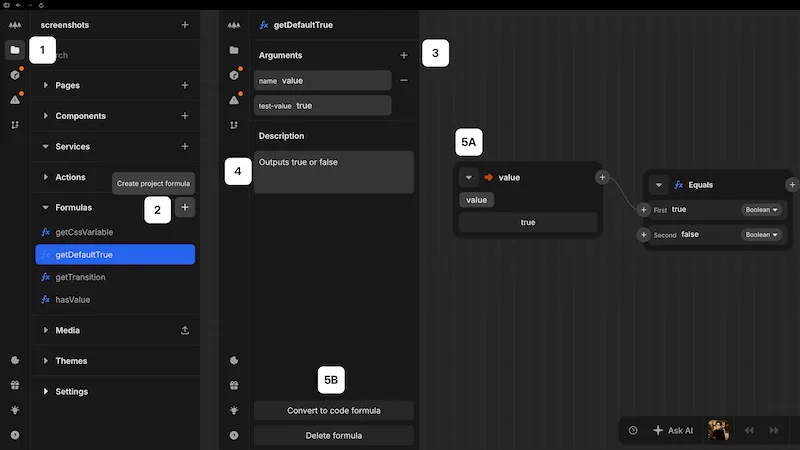
Create a project formula
Project formulas appear in the formula selection dropdown throughout your project, making them easily accessible from any component or page.
To create a project formula:
- 1Open the project sidebar by clicking the folder icon or using Cmd/Ctrl + K
- 2Find the Formulas section, click the + button and enter a name for your formula in the dialog
- 3Add arguments as input parameters with test values (optional)
- 4Add a description to your formula (optional)
- 5Define your formula logic using either
(A) The formula editor, or
(B) Click the Convert to code formula button at the bottom left of the screen to view the JavaScript code editor
Clicking Convert to code formula will not convert existing formula nodes to JavaScript code. Instead, it will switch the formula editor view to the raw code view.
Decide whether you want to use the formula editor or the custom code view before you start working in order to prevent losing any changes unexpectedly.
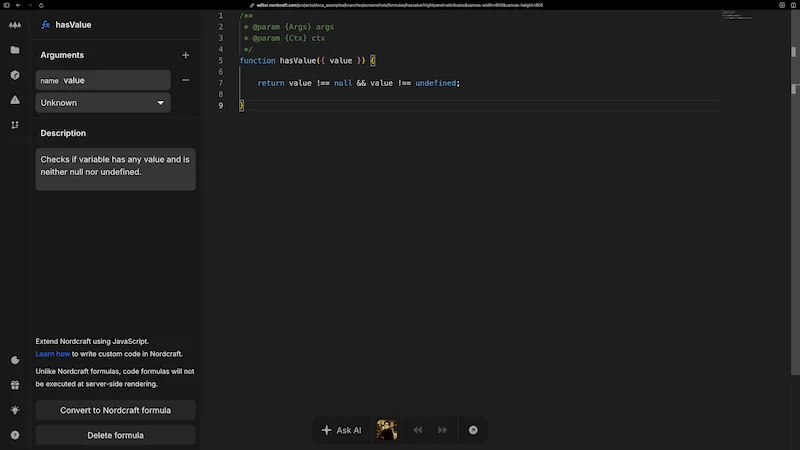
Custom code formulas
Custom code formulas extend the capabilities of the standard formula editor by allowing you to write JavaScript directly. This enables you to implement functionality that isn't available through the built-in formula components.
Custom code structure
In the custom code editor, your formula must have an entry function with the same name as your formula. This function receives two parameters:
args: The defined input parameters passed to your formulactx: The context object that provides access to Nordcraft-specific functionality
Custom code considerations
When using custom code in project formulas, keep these important points in mind:
- Pure functions: Custom formulas should be pure functions without side effects; given the same inputs, they should always return the same outputs without modifying external state
- Client-side only: Custom code formulas execute in the browser only and not during server-side rendering; this can cause layout shifts during page load and may impact your page performance scores, and as a result, SEO
- Synchronous execution: Custom formulas must be synchronous; do not use
Promise,fetchor other asynchronous JavaScript APIs in project formulas - Shadow DOM compatibility: When components are exported as web components, use
ctx.rootinstead ofdocumentto access DOM elements; this ensures compatibility with Shadow DOM encapsulation
Avoid adding side effects in custom formulas. Side effects can cause unpredictable behavior and should be handled by actions instead.
Be cautious when pasting code snippets from external sources into custom formulas. Custom code can execute any JavaScript you add, which may introduce security vulnerabilities if you do not trust the source.